|
Doxygen
1.9.8
|
|
Doxygen
1.9.8
|
Wrappers around custom CUDA kernels to handle domain transforms and basis evaluations, the kernels are instantiated in tsgCudaKernels.cu. More...
Functions | |
| template<typename scalar_type > | |
| void | solveLSmultiGPU (AccelerationContext const *acceleration, int n, int m, scalar_type A[], int nrhs, scalar_type B[]) |
| Least squares solver with data sitting on the gpu device. | |
| template<typename scalar_type > | |
| void | solveLSmultiOOC (AccelerationContext const *acceleration, int n, int m, scalar_type A[], int nrhs, scalar_type B[]) |
| Identical to TasGpu::solveLSmultiGPU() but the arrays are on the CPU and the MAGMA out-of-core implementation is used. | |
| template<typename scalar_type > | |
| void | solveLSmulti (AccelerationContext const *acceleration, int n, int m, scalar_type A[], int nrhs, scalar_type B[]) |
| Identical to TasGpu::solveLSmultiGPU() but the data starts with the CPU and gets uploaded to the GPU first. | |
| void | factorizePLU (AccelerationContext const *acceleration, int n, double A[], int_gpu_lapack ipiv[]) |
| Factorize | |
| void | solvePLU (AccelerationContext const *acceleration, char trans, int n, double const A[], int_gpu_lapack const ipiv[], double b[]) |
| Solve A x = b using a PLU factorization. | |
| void | solvePLU (AccelerationContext const *acceleration, char trans, int n, double const A[], int_gpu_lapack const ipiv[], int nrhs, double B[]) |
| Solve A x = b using a PLU factorization, B is in row-major format. | |
| template<typename scalar_type > | |
| void | denseMultiply (AccelerationContext const *acceleration, int M, int N, int K, typename GpuVector< scalar_type >::value_type alpha, GpuVector< scalar_type > const &A, GpuVector< scalar_type > const &B, typename GpuVector< scalar_type >::value_type beta, scalar_type C[]) |
| Wrapper to GPU BLAS that multiplies dense matrices (e.g., cuBlas, MAGMA). | |
| template<typename scalar_type > | |
| void | denseMultiplyMixed (AccelerationContext const *acceleration, int M, int N, int K, typename GpuVector< scalar_type >::value_type alpha, GpuVector< scalar_type > const &A, scalar_type const B[], typename GpuVector< scalar_type >::value_type beta, scalar_type C[]) |
| Identical to TasGpu::denseMultiply() but both B and C are array in CPU memory. | |
| template<typename scalar_type > | |
| void | sparseMultiply (AccelerationContext const *acceleration, int M, int N, int K, typename GpuVector< scalar_type >::value_type alpha, const GpuVector< scalar_type > &A, const GpuVector< int > &pntr, const GpuVector< int > &indx, const GpuVector< scalar_type > &vals, scalar_type C[]) |
| Wrapper to GPU methods that multiplies a sparse and a dense matrix. | |
| template<typename T > | |
| void | sparseMultiplyMixed (AccelerationContext const *acceleration, int M, int N, int K, typename GpuVector< T >::value_type alpha, const GpuVector< T > &A, const std::vector< int > &pntr, const std::vector< int > &indx, const std::vector< T > &vals, T C[]) |
| Identical to TasGpu::sparseMultiply() but the sparse matrix and the result C are in CPU memory. | |
Wrappers around custom CUDA kernels to handle domain transforms and basis evaluations, the kernels are instantiated in tsgCudaKernels.cu.
| void TasGrid::TasGpu::solveLSmultiGPU | ( | AccelerationContext const * | acceleration, |
| int | n, | ||
| int | m, | ||
| scalar_type | A[], | ||
| int | nrhs, | ||
| scalar_type | B[] | ||
| ) |
Least squares solver with data sitting on the gpu device.
Solves the least squares problem 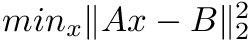
| void TasGrid::TasGpu::denseMultiply | ( | AccelerationContext const * | acceleration, |
| int | M, | ||
| int | N, | ||
| int | K, | ||
| typename GpuVector< scalar_type >::value_type | alpha, | ||
| GpuVector< scalar_type > const & | A, | ||
| GpuVector< scalar_type > const & | B, | ||
| typename GpuVector< scalar_type >::value_type | beta, | ||
| scalar_type | C[] | ||
| ) |
Wrapper to GPU BLAS that multiplies dense matrices (e.g., cuBlas, MAGMA).
Computes 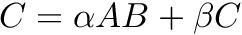
| void TasGrid::TasGpu::sparseMultiply | ( | AccelerationContext const * | acceleration, |
| int | M, | ||
| int | N, | ||
| int | K, | ||
| typename GpuVector< scalar_type >::value_type | alpha, | ||
| const GpuVector< scalar_type > & | A, | ||
| const GpuVector< int > & | pntr, | ||
| const GpuVector< int > & | indx, | ||
| const GpuVector< scalar_type > & | vals, | ||
| scalar_type | C[] | ||
| ) |
Wrapper to GPU methods that multiplies a sparse and a dense matrix.
Computes